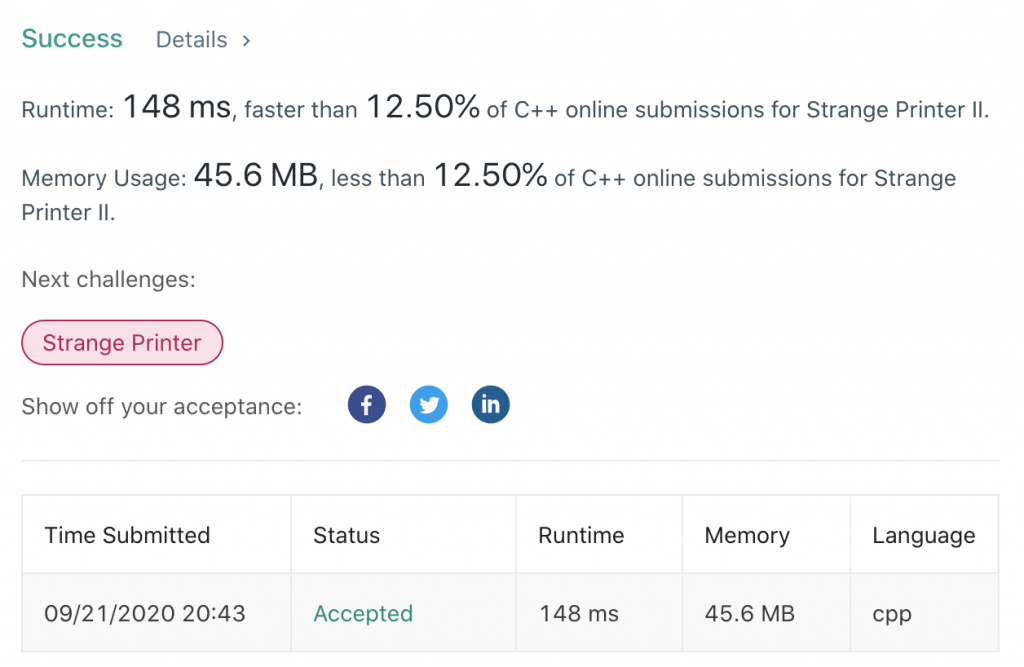
Description

Submission
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> next;
int visited[61];
bool dfs(int cur)
{
if (visited[cur]==1) return true;
visited[cur] = 2;
for (int next: next[cur])
{
if (visited[next]==1) continue;
if (visited[next]==2) return false;
if (dfs(next)==false) return false;
}
visited[cur] = 1;
return true;
}
public:
bool isPrintable(vector<vector<int>>& targetGrid) {
int nRow = targetGrid.size();
int nCol = targetGrid[0].size();
vector<int> left(61, nCol);
vector<int> right(61, -1);
vector<int> top(61, nRow);
vector<int> bottom(61, -1);
// find the boundaries
for(int i = 0; i < nRow; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < nCol; ++j) {
int color = targetGrid[i][j];
left[color] = min(left[color], j);
right[color] = max(right[color], j);
top[color] = min(top[color], i);
bottom[color] = max(bottom[color], i);
}
}
next.resize(61);
// construct the graph
for(int i = 0; i < nRow; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < nCol; ++j) {
for(int color = 1; color <= 60; ++color) {
// if inside the rectangle of a color
if(i >= top[color] && i <= bottom[color] &&
j >= left[color] && j <= right[color]) {
// if the color is other than the current color
if(color != targetGrid[i][j]) {
next[targetGrid[i][j]].push_back(color);
}
}
}
}
}
// check if there's a loop
for(int i = 1; i <= 60; ++i) {
if(dfs(i) == false) return false;
}
return true;
}
};