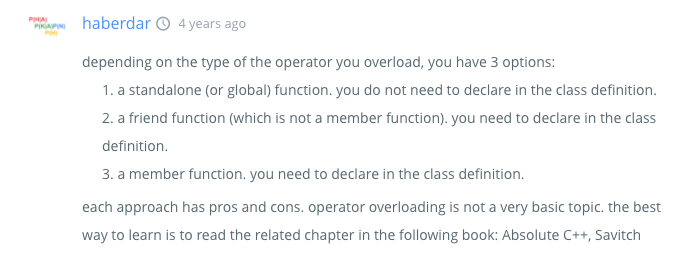
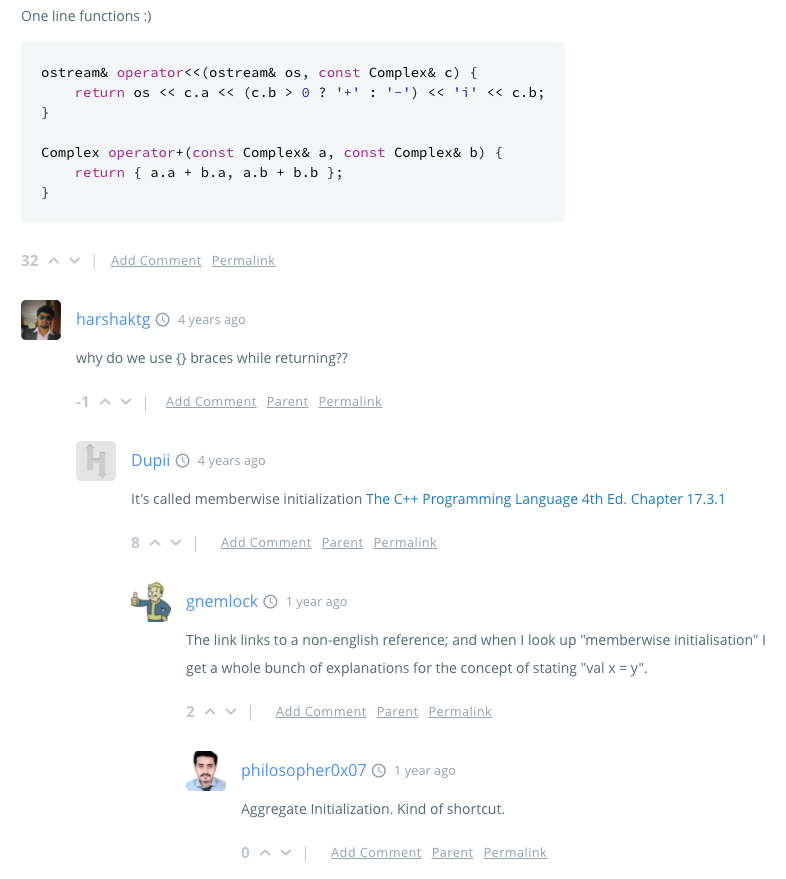
With {}, you can initialize a class without having to have a constructor.
//Operator Overloading
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
public:
int a,b;
void input(string s)
{
int v1=0;
int i=0;
while(s[i]!='+')
{
v1=v1*10+s[i]-'0';
i++;
}
while(s[i]==' ' || s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='i')
{
i++;
}
int v2=0;
while(i<s.length())
{
v2=v2*10+s[i]-'0';
i++;
}
a=v1;
b=v2;
}
};
//Overload operators + and << for the class complex
//+ should add two complex numbers as (a+ib) + (c+id) = (a+c) + i(b+d)
//<< should print a complex number in the format "a+ib"
Complex operator+ (const Complex& lhs, const Complex& rhs)
{
return {lhs.a + rhs.a, lhs.b + rhs.b};
}
ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const Complex& c)
{
int abs_b = c.b;
string sign;
if(c.b > 0) {
sign = "+";
} else {
sign = "-";
abs_b = -c.b;
}
os << c.a << sign << "i" << abs_b << endl;
return os;
}
int main()
{
Complex x,y;
string s1,s2;
cin>>s1;
cin>>s2;
x.input(s1);
y.input(s2);
Complex z=x+y;
cout<<z<<endl;
}
References
Following are comments in the discussion forum I found valuable.