
Problem 1

Problem 2 – Shortest Path Variant 1
Write a program to not only find the weighted shortest distances but also count the number of different minimum paths from any vertex to a given source vertex in a digraph. It is guaranteed that all the weights are positive.
Format of functions:
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int count[], Vertex S );
where MGraph is defined as the following:
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
WeightType G[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
};
typedef PtrToGNode MGraph;
The shortest distance from V to the source S is supposed to be stored in dist[V]. If V cannot be reached from S, store -1 instead. The number of different minimum paths from V to the source S is supposed to be stored in count[V] and count[S]=1.
Sample program of judge:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
#define INFINITY 1000000
#define MaxVertexNum 10 /* maximum number of vertices */
typedef int Vertex; /* vertices are numbered from 0 to MaxVertexNum-1 */
typedef int WeightType;
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
WeightType G[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
};
typedef PtrToGNode MGraph;
MGraph ReadG(); /* details omitted */
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int count[], Vertex S );
int main()
{
int dist[MaxVertexNum], count[MaxVertexNum];
Vertex S, V;
MGraph G = ReadG();
scanf("%d", &S);
ShortestDist( G, dist, count, S );
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", dist[V]);
printf("\n");
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", count[V]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/* Your function will be put here */
Sample Input (for the graph shown in the figure):
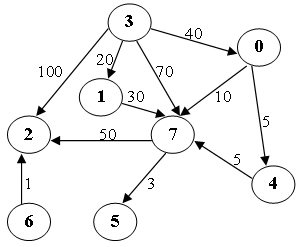
8 11 0 4 5 0 7 10 1 7 30 3 0 40 3 1 20 3 2 100 3 7 70 4 7 5 6 2 1 7 5 3 7 2 50 3
Sample Output:
40 20 100 0 45 53 -1 50 1 1 4 1 1 3 0 3
Answer:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
#define INFINITY 1000000
#define MaxVertexNum 10 /* maximum number of vertices */
typedef int Vertex; /* vertices are numbered from 0 to MaxVertexNum-1 */
typedef int WeightType;
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
WeightType G[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
};
typedef PtrToGNode MGraph;
MGraph ReadG() /* details omitted */
{
MGraph graph = (MGraph) malloc (sizeof(struct GNode));
for(int i = 0; i < MaxVertexNum; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < MaxVertexNum; j++) {
graph->G[i][j] = INFINITY;
}
}
scanf("%d %d", &(graph->Nv), &(graph->Ne));
for(int i = 0; i < graph->Ne; i++) {
int v, w, weight;
scanf("%d %d %d", &v, &w, &weight);
graph->G[v][w] = weight;
}
return graph;
}
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int count[], Vertex S );
int main()
{
int dist[MaxVertexNum], count[MaxVertexNum];
Vertex S, V;
MGraph G = ReadG();
scanf("%d", &S);
ShortestDist( G, dist, count, S );
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", dist[V]);
printf("\n");
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", count[V]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/* Your function will be put here */
Vertex MinDistance(MGraph Graph, int* count, int* dist, bool* visited)
{
int minDist = INFINITY;
// if none returned, should set rest of the count to 0
Vertex minVertex = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
if(!visited[i] && dist[i] < minDist) {
minDist = dist[i];
minVertex = i;
}
}
if(minVertex == -1) {
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
if(dist[i] == INFINITY){
dist[i] = -1;
}
}
} else {
// Dequeue the vertex
visited[minVertex] = true;
}
return minVertex;
}
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int count[], Vertex S )
{
bool visited[MaxVertexNum] = {false};
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
count[i] = 0;
visited[i] = 0;// not visited
dist[i] = INFINITY;
}
dist[S] = 0;
count[S] = 1;
// for all possible solutions
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
Vertex u = MinDistance(Graph, count, dist, visited);
if(u == -1) {
break;
}
// for all neighbors of u
for(int v = 0; v < Graph->Nv; v++) {
if(Graph->G[u][v] != INFINITY) {
if(dist[v] > dist[u] + Graph->G[u][v]){
dist[v] = dist[u] + Graph->G[u][v];
count[v] = (1 > count[u]) ? 1 : count[u];
} else if(dist[v] == dist[u] + Graph->G[u][v]) {
count[v] += count[u];
}
}
}
}
}
Problem 3 – Shortest Path Variant 2
Write a program to find the weighted shortest distances from any vertex to a given source vertex in a digraph. If there is more than one minimum path from v to w, a path with the fewest number of edges is chosen. It is guaranteed that all the weights are positive and such a path is unique for any vertex.
Format of functions:
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int path[], Vertex S );
where MGraph is defined as the following:
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
WeightType G[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
};
typedef PtrToGNode MGraph;
The shortest distance from V to the source S is supposed to be stored in dist[V]. If V cannot be reached from S, store -1 instead. If W is the vertex being visited right before V along the shortest path from S to V, then path[V]=W. If V cannot be reached from S, path[V]=-1, and we have path[S]=-1.
Sample program of judge:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
#define INFINITY 1000000
#define MaxVertexNum 10 /* maximum number of vertices */
typedef int Vertex; /* vertices are numbered from 0 to MaxVertexNum-1 */
typedef int WeightType;
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
WeightType G[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
};
typedef PtrToGNode MGraph;
MGraph ReadG(); /* details omitted */
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int path[], Vertex S );
int main()
{
int dist[MaxVertexNum], path[MaxVertexNum];
Vertex S, V;
MGraph G = ReadG();
scanf("%d", &S);
ShortestDist( G, dist, path, S );
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", dist[V]);
printf("\n");
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", path[V]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/* Your function will be put here */
Sample Input (for the graph shown in the figure):
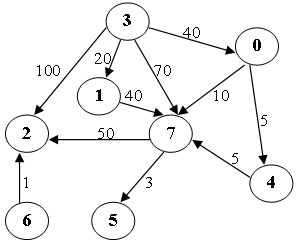
8 11 0 4 5 0 7 10 1 7 40 3 0 40 3 1 20 3 2 100 3 7 70 4 7 5 6 2 1 7 5 3 7 2 50 3
Sample Output:
40 20 100 0 45 53 -1 50 3 3 3 -1 0 7 -1 0
Answer:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
#define INFINITY 1000000
#define MaxVertexNum 10 /* maximum number of vertices */
typedef int Vertex; /* vertices are numbered from 0 to MaxVertexNum-1 */
typedef int WeightType;
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv;
int Ne;
WeightType G[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];
};
typedef PtrToGNode MGraph;
MGraph ReadG() /* details omitted */
{
MGraph graph = (MGraph) malloc (sizeof(struct GNode));
for(int i = 0; i < MaxVertexNum; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < MaxVertexNum; j++) {
graph->G[i][j] = INFINITY;
}
// G[i][i] won't be used
}
scanf("%d %d", &(graph->Nv), &(graph->Ne));
for(int i = 0; i < graph->Ne; i++) {
int v, w, weight;
scanf("%d %d %d", &v, &w, &weight);
graph->G[v][w] = weight;
}
return graph;
}
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int path[], Vertex S );
int main()
{
int dist[MaxVertexNum], path[MaxVertexNum];
Vertex S, V;
MGraph G = ReadG();
scanf("%d", &S);
ShortestDist( G, dist, path, S );
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", dist[V]);
printf("\n");
for ( V=0; V<G->Nv; V++ )
printf("%d ", path[V]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/* Your function will be put here */
Vertex MinDistance(MGraph Graph, int* dist, bool* visited)
{
int minDist = INFINITY;
// if none returned, should set rest of the count to 0
Vertex minVertex = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
if(!visited[i] && dist[i] < minDist) {
minDist = dist[i];
minVertex = i;
}
}
if(minVertex == -1) {
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
if(dist[i] == INFINITY) {
dist[i] = -1;
}
}
} else {
// Dequeue the vertex
visited[minVertex] = true;
}
return minVertex;
}
void ShortestDist( MGraph Graph, int dist[], int path[], Vertex S )
{
bool visited[MaxVertexNum] = {false};
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
dist[i] = INFINITY;
path[i] = -1;
}
dist[S] = 0;
// maximum possible number of loops
for(int i = 0; i < Graph->Nv; i++) {
Vertex u = MinDistance(Graph, dist, visited);
if(u < 0) {
break;
}
// for all vertices v connected to u
for(int v = 0; v < Graph->Nv; v++) {
if(Graph->G[u][v] && dist[v] > dist[u] + Graph->G[u][v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + Graph->G[u][v];
path[v] = u;
}
}
}
}